Porter’s Five forces analysis
Porter’s five forces model is an analysis tool that uses five industry forces to determine the intensity of competition in an industry and its profitability level.
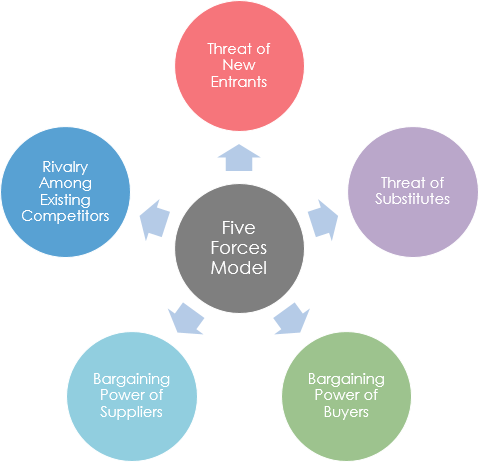
These forces determine an industry structure and the level of competition in that industry. The stronger competitive forces in the industry are the less profitable it is. An industry with low barriers to enter, having few buyers and suppliers but many substitute products and competitors will be seen as very competitive and thus, not so attractive due to its low profitability.
We now understand that Porter’s five forces framework is used to analyze the industry’s competitive forces and to shape the organization’s strategy according to the results of the analysis. But how to use this tool? We have identified the following steps:
- Step 1. Gather the information on each of the five forces
- Step 2. Analyze the results and display them on a diagram
- Step 3. Formulate strategies based on the conclusions
Step 1. Gather the information on each of the five forces. What managers should do during this step is to gather information about their industry and to check it against each of the factors (such as “number of competitors in the industry”) influencing the force. We have already identified the most important factors in the table below.
Porter’s Five Forces FactorsThreat of new entry
- Amount of capital required
- Retaliation by existing companies
- Legal barriers (patents, copyrights, etc.)
- Brand Reputation
- Product differentiation
- Access to suppliers and distributors
- Economies of scale
- Sunk costs
- Government regulation
Supplier power
- Number of suppliers
- Suppliers’ size
- Ability to find substitute materials
- Materials scarcity
- Cost of switching to alternative materials
- The threat of integrating forward
Buyer power
- Number of buyers
- Size of buyers
- Size of each order
- Buyers’ cost of switching suppliers
- There are many substitutes
- Price sensitivity
- The threat of integrating backwards
Threat of substitutes
- Number of substitutes
- Performance of substitutes
- Cost of changing
Rivalry among existing competitors
- Number of competitors
- Cost of leaving an industry
- Industry growth rate and size
- Product differentiation
- Competitors’ size
- Customer loyalty
- The threat of horizontal integration
- Level of advertising expense
Step 2. Analyze the results and display them on a diagram. After gathering all the information, you should analyze it and determine how each force is affecting an industry. For example, if there are many companies of equal size operating in the slow growth industry, it means that rivalry between existing companies is strong. Remember that five forces affect different industries differently so don’t use the same results of an analysis for even similar industries!
Step 3. Formulate strategies based on the conclusions. At this stage, managers should formulate firm’s strategies using the results of the analysis, For example, if it is hard to achieve economies of scale in the market, the company should pursue cost leadership strategy. Product development strategy should be used if the current market growth is slow and the market is saturated.
Although Porter’s five forces is a great tool to analyze industry’s structure and use the results to formulate firm’s strategy, it has its limitations and requires further analysis to be done, such as SWOT, PEST or Value Chain analysis.
Sukant Kumar is a Product / Marketing leader in tech. I am passionate about tech and product and creating memorable user experiences. Connect with me on LinkedIn, mentioning this story. If you liked this story do let me know in comments and don’t forget to clap a dozen times 😎
